AB SCIEX Analyst
Analyst is the data acquisition software for AB Sciex QTrap, triple quadrupole (formerly QStar), and TripleTOF (5600) LC/MS/MS Systems.
There are several options available for processing raw data into peak lists for searching with Mascot.
mascot.dll is an Analyst "script" that can be invoked from within Analyst or used as a data
import filter by Mascot Daemon for batch processing of Wiff files. Peak picking is fast,
but mascot.dll isn't compatible with quantitation using Mascot Distiller.
MS Data Converter is the AB Sciex command line utility to export data in mzML and MGF formats.
An MGF file is the most compact format for submission to Mascot. The mzML format is more verbose, but
can be opened in Mascot Distiller for searching, de novo sequencing, and quantitation.
Mascot Distiller can open the original Wiff files or the mzML files exported by the AB Sciex MS Data Converter.
Like mascot.dll, Distiller can be used as a data import filter by Mascot Daemon for batch processing of files. The advantage of using
Distiller is that it provides comprehensive support for quantitation.
The latest version of the Mascot script for Analyst can be downloaded here:
Before installing mascot.dll, you should verify that Analyst has the latest
hot fixes
applied.
There are some troubleshooting tips below.
Interactive Searching
When used interactively, the Mascot script performs data reduction of MS and MS/MS data, creating a Mascot
Generic Format (MGF) peak list, and invoking a Mascot search form with the peak list file pre-selected.
The Mascot server can be either the public web site or an in-house server.
Full details of the dialogs and options can be found in mascot.doc, which is copied to the Analyst help directory
during installation. Briefly, the available options depend on the contents of the active Analyst pane at the time the
script is invoked. (NB The display must be the standard 'TIC' display, not IDA Explorer).
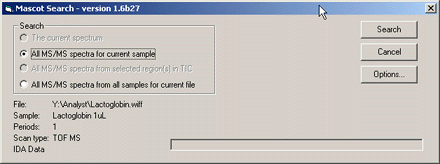
- The current spectrum If the active Analyst pane is a centroided spectrum, (either MS or MS/MS),
this option can be used to search just that spectrum
- All MS-MS spectra in the file This option can be used to perform time domain processing of all
the MS/MS spectra from a single sample. That is, MS/MS spectra from the same precursor, eluting within a
specified time interval, will be summed together
- All MS-MS spectra from selected region in TIC If the active Analyst pane is a TIC that contains a
selected region, this option can be used to perform time domain processing over just the selected region.
This can speed up the processing time if only a portion of the run is known to contain useful data
- All MS-MS spectra from all samples This option can be used to perform time domain processing of
all the MS/MS spectra for all samples in a multi-sample WIFF file
Clicking on the Options... button displays the processing options for data reduction.
Tooltip help is provided for most options.
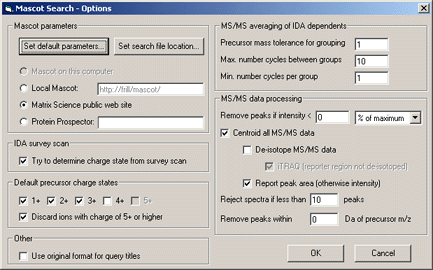
The 'Set default parameters' button displays Mascot 'Set Defaults' form , allowing you to define default
search form settings.
Note:If you are processing iTRAQtm data,
and choose to 'De-isotope MS/MS data', make sure you also choose
'iTRAQ (reporter region not deisotoped)'.
Automation using Mascot Daemon
Mascot Daemon can use mascot.dll as a data import filter, eliminating the need to
create peak lists from WIFF files manually. To use this facility, first create a suitable parameter
set and save it. The Data format should be specified as Mascot Generic.
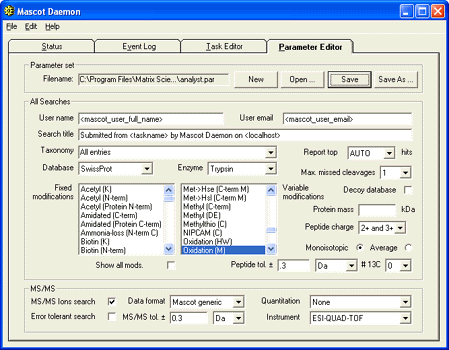
In the Task editor, Choose the 'AB | MDS Sciex Analyst .WIFF file' option from the data import filters. This
option will be available if mascot.dll is installed and registered on the PC running Mascot Daemon.
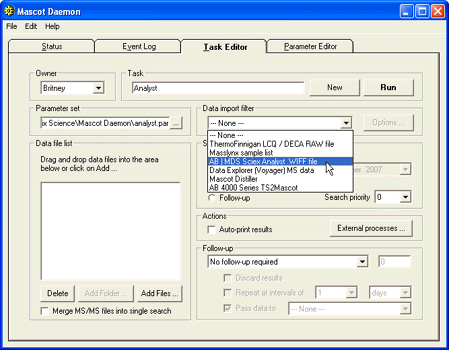
Clicking on the Options button will invoke a dialog that is very similar to the interactive mascot.dll
dialog.

Press OK to save the options, and then continue to set up either a batch or real-time monitor task.
Note that when the task is run, the options settings are saved as defaults for next time, but each task can
have different options settings.
Real-time Monitor Mode
One type of Daemon task is a batch task, where a list of WIFF files is searched immediately, or at some pre-set
time. Alternatively, it can be a
real-time monitor task, monitoring a specified path for new WIFF files. The advantage of a real-time monitor
task is that data files can be submitted to Mascot immediately after acquisition and without any user intervention.
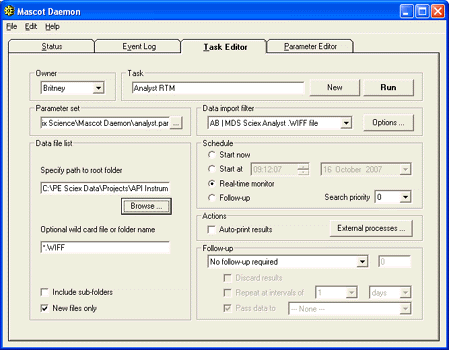
In real-time monitor mode, it is important that Mascot Daemon waits until a file is complete before
submitting it to Mascot. To avoid taking a file that is still being written, it checks the file size
at intervals, and waits until it has stopped increasing. The default interval is 60 seconds, which works
fine in most cases, but may not be long enough if there are periods when the WIFF file size
grows only slowly. If you observe that Daemon is submitting a search before the WIFF file is complete,
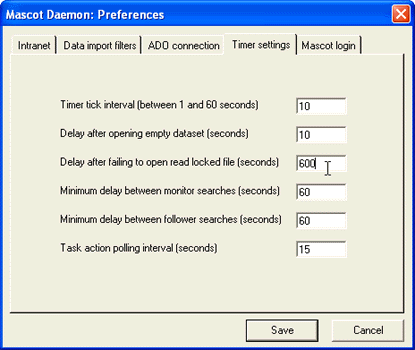
increase the interval by going to the
Timer Settings tab of the Preferences dialog. Increase the value of 'Delay after failing to open
read-locked file' from 60 seconds to (say) 600 seconds.
In order to import WIFF files in Mascot Daemon, both Analyst and mascot.dll must be installed on the same
PC as Daemon. If you still don't see the 'AB | MDS Sciex Analyst .WIFF file' option on the data import
filter drop-down list, or if you see the following error message, then you either have an old version of
mascot.dll, or it is not installed and registered correctly.
Run-time error '430':
Class does not support automation or does not support expected interface
The fix is to download and install the latest version of
mascot.dll.
If you get the message:
Cannot load driver library FMWIFFCompDocNTDriver.dll
Make sure the DLL is in your path or in the same directory as your .exe
<C:\program files\daemon\daemon.exe>
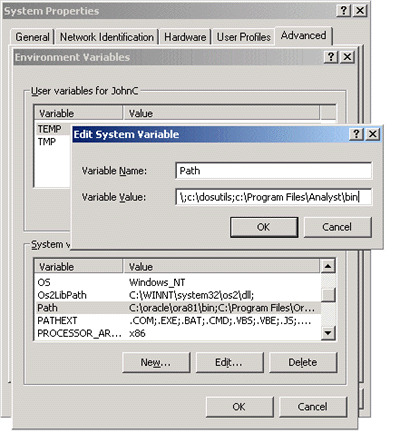
The problem is that the Analyst\bin directory is not on your path. Go to the Windows System
Control panel and choose the Advanced tab. Select Environment Variables, and add the full path to the
Analyst\bin directory to the end of the path. You may have to re-boot the system for the change
to take effect.
The MS Data Converter is a free download from AB Sciex.
It supports both Wiff files and TOF/TOF data stored in an Oracle database. Output can be a simple MGF peak list
or an mzML file containing a fairly complete representation of the raw data.
For rapid peak picking, the converter exports the centroids determined by the instrument
software during acquisition. For Wiff files, there is also an option to use the peak picking algorithm
from ProteinPilot. This gives particularly good results on TripleTOF (5600) data. If you plan to use
Distiller for quantitation, but would like to have the ProteinPilot peak list for the database search,
this can be achieved by exporting the data as an mzML file. You cannot choose to peak pick the MS/MS scans
and keep the survey scans as raw profile data, so this means that the survey scans are also
exported as centroids, and must be uncentroided by Distiller. This is not ideal, but does not
create any noticeable problems in the examples of 5600 data that we have studied.
The command line to convert a Wiff file to an mzML file with ProteinPilot peak picking will be similar to this:
AB_SCIEX_MS_Converter.exe WIFF C:\tmp\fraction_42.wiff
-proteinpilot MZML C:\tmp\fraction_42.mzml
(Remember to use double quotes around the file paths if they include any spaces.) When the mzML file is opened in
Distiller, you need to choose processing options that uncentroid the survey scans but take the existing centroid
values from the MS/MS scans, for example mzml_centroided.opt.
The converter also allows profile data to be exported to an mzML file.
If you intend to open the file in Distiller, you need to add an undocumented switch to the command line,
/zeropadding, to preserve data points with zero intensity. For example
AB_SCIEX_MS_Converter.exe WIFF C:\tmp\fraction_42.wiff
-profile MZML C:\tmp\fraction_42.mzml /zeropadding
If you do not do this, you will observe artefacts like this in weak spectra, which compromise peak picking:
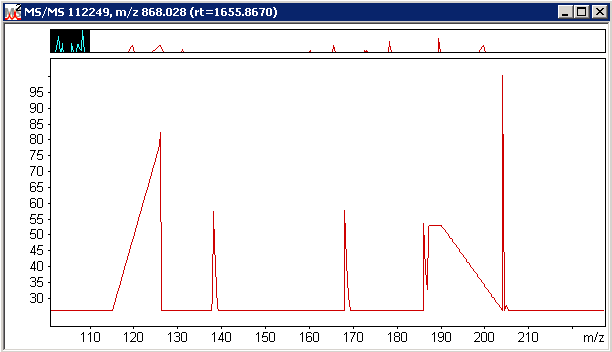
When the /zeropadding flag is used, the mzML files are huge, typically a factor of 50 or more larger than the
corresponding Wiff file.
If you want to work with raw profile data in Distiller, much better to work with the original Wiff file.
Mascot Distiller can be used to browse
Wiff files, and process them into high quality peak
lists that can be saved or submitted direct to a Mascot Server for searching.
With the appropriate Distiller Toolboxes, the search results can be imported back into Distiller for
further examination or used as the basis for quantitation. If the optional Mascot Daemon Toolbox is
installed, these processes can be automated using Mascot Daemon.
With high resolution data from a 5600, peak picking in Distiller can be slow because of the large number of scans,
each of which has a very large number of data points. An alternative is to use the AB Sciex
MS Data Converter to perform the peak picking, saving the centroids to an mzML
file that can be opened in Distiller, as described above.
If you prefer to work from the Wiff files, suitable peak picking options for 5600 data are
here: 5600.opt.
You may wish to change the maximum charge state for precursors; the higher this setting, the longer peak
picking will take. The peaks in individual MS/MS spectra can be weak, making it difficult for Distiller to fit
isotopic distributions, and you may find you get better database search results by selecting to pick individual
peaks in the MS/MS scans, rather than complete isotope distributions: 5600_SPP.opt.
Some degree of isotopic resolution is essential for good quantitation. If you plan to use QTrap data for
MS-based quantitation, such as SILAC, 18O, or ICAT, isotopic resolution can be obtained by using Enhanced Resolution (ER) scans.
Typically, there will only be one or two ER scans for each precursor, compared with many survey scans across the
elution profile, but the advantage of getting isotopic resolution outweighs this. Compare these scans from a 4000 QTrap for
a precursor in an 18O experiment.
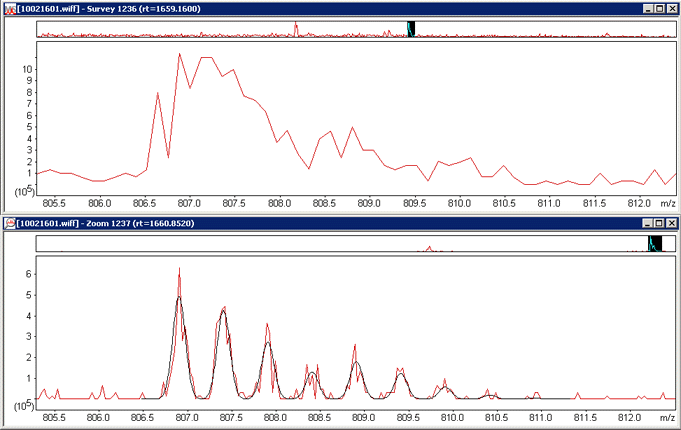
Without isotopic resolution it is not possible to deconvolute the overlapping isotope distributions with any reliability.
While an ER scan may be a one-shot measurement, it enables a calculated distribution (in black) to be fitted to the experimental
data (in red) giving confidence that the true relative peak areas are being measured. Distiller processing options for this
particular file were qtrap_zoom.opt. The choice of whether to use survey
or ER scans for quantitation is an option in the quantitation method.
|